用 OpenVINO™ 在 Intel 13th Gen CPU 上运行 SDXL-Turbo 文本图像生成模型
 openlab_96bf3613
更新于 2月前
openlab_96bf3613
更新于 2月前
作者:英特尔创新大使 卢雨畋
本文基于 13th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-13490F 型号 CPU 验证,对于量化后模型,你只需要在 16G 的笔记本电脑上就可体验生成过程(最佳体验为32G内存)。
SDXL-Turbo是一个快速的生成式文本到图像模型,可以通过单次网络评估从文本提示中合成逼真的图像。SDXL-Turbo采用了一种称为Adversarial Diffusion Distillation (ADD)的新型训练方法(详见技术报告),该方法可以在1到4个步骤中对大规模基础图像扩散模型进行采样,并保持高质量的图像。通过最新版本(2023.2)OpenVINO™ 工具套件的强大推理能力及 NNCF 的高效神经网络压缩能力,我们能够在两秒内实现 SDXL-Turbo 图像的高速、高质量生成。
环境安装
在开始之前,我们需要安装所有环境依赖:
%pip install --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu \
torch transformers diffusers nncf optimum-intel gradio openvino==2023.2.0 onnx "git+https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-intel.git" 下载、转换模型
首先我们要把 huggingface 下载的原始模型转化为 OpenVINO IR,以便后续的 NNCF 工具链进行量化工作。转换完成后你将得到对应的 text_encode、unet、vae模型。
from pathlib import Path
model_dir = Path("./sdxl_vino_model")
sdxl_model_id = "stabilityai/sdxl-turbo"
skip_convert_model = model_dir.exists()
import os
if not skip_convert_model:
# 设置下载路径到当前文件夹,并加速下载
os.environ['HF_ENDPOINT'] = 'https://hf-mirror.com'
os.system(f'optimum-cli export openvino --model {sdxl_model_id} --task stable-diffusion-xl {model_dir} --fp16')
os.environ['HF_ENDPOINT'] = 'https://hf-mirror.com'
tae_id = "madebyollin/taesdxl"
save_path = './taesdxl'
os.system(f'huggingface-cli download --resume-download {tae_id} --local-dir {save_path}') import torch
import openvino as ov
from diffusers import AutoencoderTiny
import gc
class VAEEncoder(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, sample):
return self.vae.encode(sample)
class VAEDecoder(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vae):
super().__init__()
self.vae = vae
def forward(self, latent_sample):
return self.vae.decode(latent_sample)
def convert_tiny_vae(save_path, output_path):
tiny_vae = AutoencoderTiny.from_pretrained(save_path)
tiny_vae.eval()
vae_encoder = VAEEncoder(tiny_vae)
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_encoder, example_input=torch.zeros((1,3,512,512)))
ov.save_model(ov_model, output_path / "vae_encoder/openvino_model.xml")
tiny_vae.save_config(output_path / "vae_encoder")
vae_decoder = VAEDecoder(tiny_vae)
ov_model = ov.convert_model(vae_decoder, example_input=torch.zeros((1,4,64,64)))
ov.save_model(ov_model, output_path / "vae_decoder/openvino_model.xml")
tiny_vae.save_config(output_path / "vae_decoder")
convert_tiny_vae(save_path, model_dir) 从文本到图像生成
现在,我们就可以进行文本到图像的生成了,我们使用优化后的 openvino pipeline 加载转换后的模型文件并推理;只需要指定一个文本输入,就可以生成我们想要的图像结果。
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline
device='AUTO' # 这里直接指定AUTO,可以写成CPU
model_dir = "./sdxl_vino_model"
text2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir, device=device) import numpy as np
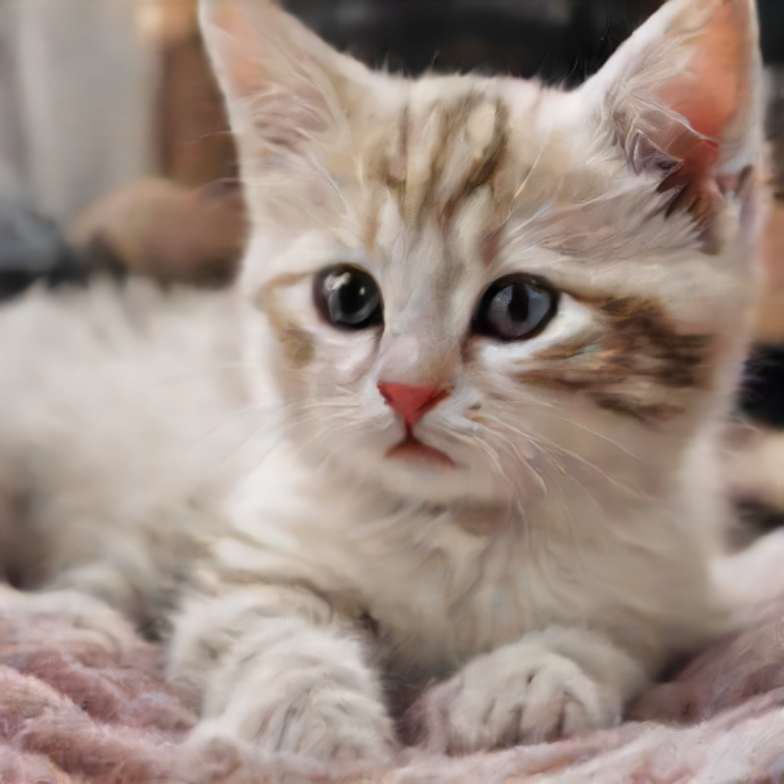
prompt = "cute cat"
image = text2image_pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=1, height=512, width=512, guidance_scale=0.0, generator=np.random.RandomState(987)).images[0]
image.save("cat.png")
image # 清除资源占用
import gc
del text2image_pipe
gc.collect() 从图片到图片生成
我们还可以实现从图片到图片的扩散模型生成,将刚才产出的文生图图片进行二次图像生成即可。
from optimum.intel import OVStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline
model_dir = "./sdxl_vino_model"
device='AUTO' # 'CPU'
image2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir, device=device) Compiling the vae_decoder to AUTO ...
Compiling the unet to AUTO ...
Compiling the vae_encoder to AUTO ...
Compiling the text_encoder_2 to AUTO ...
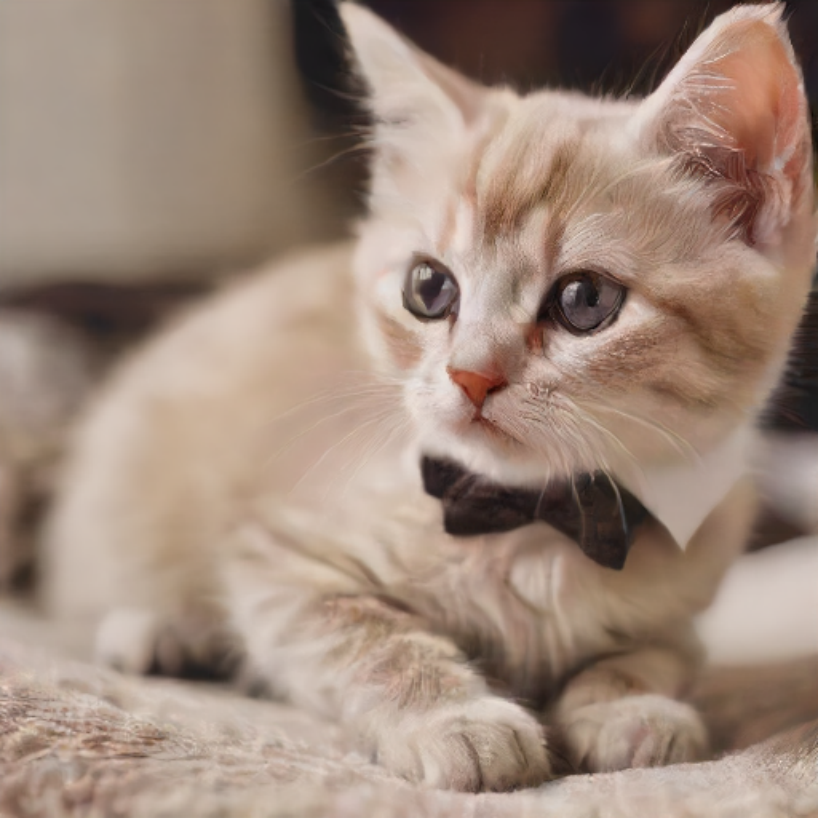
Compiling the text_encoder to AUTO ... photo_prompt = "a cute cat with bow tie"
photo_image = image2image_pipe(photo_prompt, image=image, num_inference_steps=2, generator=np.random.RandomState(511), guidance_scale=0.0, strength=0.5).images[0]
photo_image.save("cat_tie.png")
photo_image 量化
NNCF(Neural Network Compression Framework)是一款神经网络压缩框架,通过对OpenVINO IR格式模型的压缩与量化巍以便更好的提升模型在 Intel 设备上部署的推理性能。
[NNCF](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/nncf/) 通过在模型图中添加量化层,并使用训练数据集的子集来微调这些额外的量化层的参数,实现了后训练量化。量化后的权重结果将是 INT8 而不是 FP32/FP16,从而加快了模型的推理速度。
根据 SDXL-Turbo Model 的结构,UNet 模型占据了整个流水线执行时间的重要部分。现在我们将展示如何使用 [NNCF](https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/nncf/) 对 UNet 部分进行优化,以减少计算成本并加快流水线速度。至于其余部分不需要量化,因为并不能显著提高推理性能,但可能会导致准确性的大幅降低。
量化过程包含以下步骤:
- 为量化创建一个校准数据集。
- 运行 nncf.quantize() 来获取量化模型。
- 使用 openvino.save_model() 函数保存 INT8 模型。
注:由于量化需要一定的硬件资源(64G以上的内存),之后我直接附上了量化后的模型,你可以直接下载使用。
from pathlib import Path
import openvino as ov
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline
import os
core = ov.Core()
model_dir = Path("./sdxl_vino_model")
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = model_dir / "optimized_unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
import datasets
import numpy as np
from tqdm import tqdm
from transformers import set_seed
from typing import Any, Dict, List
set_seed(1)
class CompiledModelDecorator(ov.CompiledModel):
def __init__(self, compiled_model: ov.CompiledModel, data_cache: List[Any] = None):
super().__init__(compiled_model)
self.data_cache = data_cache if data_cache else []
def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.data_cache.append(*args)
return super().__call__(*args, **kwargs)
def collect_calibration_data(pipe, subset_size: int) -> List[Dict]:
original_unet = pipe.unet.request
pipe.unet.request = CompiledModelDecorator(original_unet)
dataset = datasets.load_dataset("conceptual_captions", split="train").shuffle(seed=42)
# Run inference for data collection
pbar = tqdm(total=subset_size)
diff = 0
for batch in dataset:
prompt = batch["caption"]
if len(prompt) > pipe.tokenizer.model_max_length:
continue
_ = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=1,
height=512,
width=512,
guidance_scale=0.0,
generator=np.random.RandomState(987)
)
collected_subset_size = len(pipe.unet.request.data_cache)
if collected_subset_size >= subset_size:
pbar.update(subset_size - pbar.n)
break
pbar.update(collected_subset_size - diff)
diff = collected_subset_size
calibration_dataset = pipe.unet.request.data_cache
pipe.unet.request = original_unet
return calibration_dataset if not UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
text2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir)
unet_calibration_data = collect_calibration_data(text2image_pipe, subset_size=200) import nncf
from nncf.scopes import IgnoredScope
UNET_OV_PATH = model_dir / "unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
if not UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.exists():
unet = core.read_model(UNET_OV_PATH)
quantized_unet = nncf.quantize(
model=unet,
model_type=nncf.ModelType.TRANSFORMER,
calibration_dataset=nncf.Dataset(unet_calibration_data),
ignored_scope=IgnoredScope(
names=[
"__module.model.conv_in/aten::_convolution/Convolution",
"__module.model.up_blocks.2.resnets.2.conv_shortcut/aten::_convolution/Convolution",
"__module.model.conv_out/aten::_convolution/Convolution"
],
),
)
ov.save_model(quantized_unet, UNET_INT8_OV_PATH) 运行量化后模型
由于量化 unet 的过程需要的内存可能比较大,且耗时较长,我提前导出了量化后 unet 模型,此处给出下载地址:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1WMAsgFFkKKp-EAS6M1wK1g 提取码: psta
下载后解压到目标文件夹 `sdxl_vino_model` 即可运行量化后的 int8 unet 模型。
从文本到图像生成
from pathlib import Path
import openvino as ov
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline
import numpy as np
core = ov.Core()
model_dir = Path("./sdxl_vino_model")
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = model_dir / "optimized_unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
int8_text2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir, compile=False)
int8_text2image_pipe.unet.model = core.read_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
int8_text2image_pipe.unet.request = None
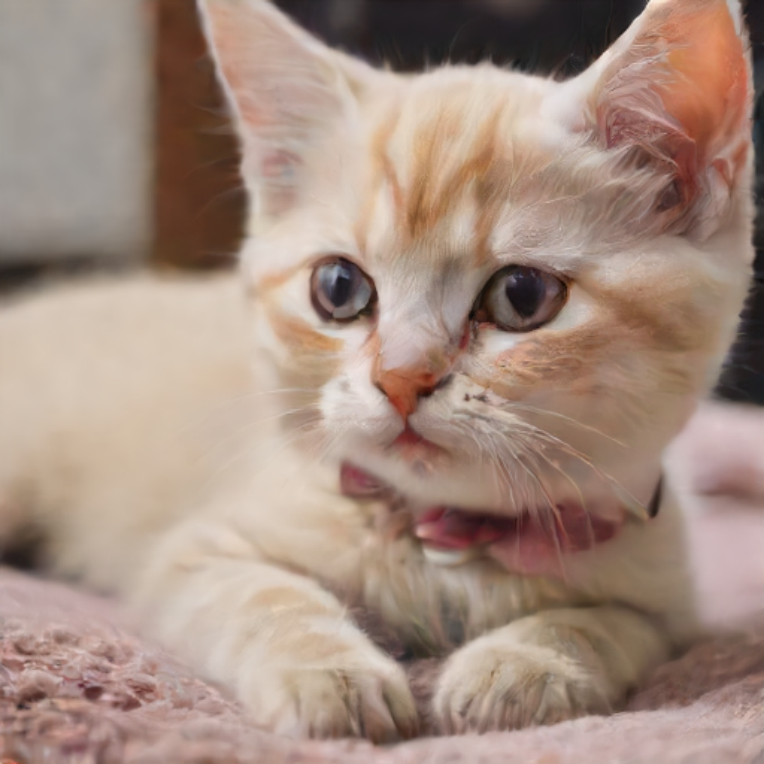
prompt = "cute cat"
image = int8_text2image_pipe(prompt, num_inference_steps=1, height=512, width=512, guidance_scale=0.0, generator=np.random.RandomState(987)).images[0]
display(image) Compiling the text_encoder to CPU ...
Compiling the text_encoder_2 to CPU ...
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Compiling the unet to CPU ...
Compiling the vae_decoder to CPU ... 从图片到图片生成
from optimum.intel import OVStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline
int8_image2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLImg2ImgPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir, compile=False)
int8_image2image_pipe.unet.model = core.read_model(UNET_INT8_OV_PATH)
int8_image2image_pipe.unet.request = None
photo_prompt = "a cute cat with bow tie"
photo_image = int8_image2image_pipe(photo_prompt, image=image, num_inference_steps=2, generator=np.random.RandomState(511), guidance_scale=0.0, strength=0.5).images[0]
display(photo_image)
Compiling the text_encoder to CPU ...
Compiling the text_encoder_2 to CPU ...
Compiling the vae_encoder to CPU ...
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
Compiling the unet to CPU ...
Compiling the vae_decoder to CPU ...
我们可以对比量化后的 unet 模型大小减少,可以看到量化对模型大小的压缩是非常显著的
from pathlib import Path
model_dir = Path("./sdxl_vino_model")
UNET_OV_PATH = model_dir / "unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
UNET_INT8_OV_PATH = model_dir / "optimized_unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
fp16_ir_model_size = UNET_OV_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
quantized_model_size = UNET_INT8_OV_PATH.with_suffix(".bin").stat().st_size / 1024
print(f"FP16 model size: {fp16_ir_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"INT8 model size: {quantized_model_size:.2f} KB")
print(f"Model compression rate: {fp16_ir_model_size / quantized_model_size:.3f}") FP16 model size: 5014578.27 KB
INT8 model size: 2513501.39 KB
Model compression rate: 1.995 运行下列代码可以对量化前后模型推理速度进行简单比较,我们可以发现速度几乎加速了一倍,NNCF 使我们在CPU上生成一张图的时间缩短到两秒之内:
FP16 pipeline latency: 3.148
INT8 pipeline latency: 1.558
Text-to-Image generation speed up: 2.020 import time
def calculate_inference_time(pipe):
inference_time = []
for prompt in ['cat']*10:
start = time.perf_counter()
_ = pipe(
prompt,
num_inference_steps=1,
guidance_scale=0.0,
generator=np.random.RandomState(23)
).images[0]
end = time.perf_counter()
delta = end - start
inference_time.append(delta)
return np.median(inference_time) int8_latency = calculate_inference_time(int8_text2image_pipe)
text2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir)
fp_latency = calculate_inference_time(text2image_pipe)
print(f"FP16 pipeline latency: {fp_latency:.3f}")
print(f"INT8 pipeline latency: {int8_latency:.3f}")
print(f"Text-to-Image generation speed up: {fp_latency / int8_latency:.3f}") 可交互前端demo
最后,为了方便推理使用,这里附上了 gradio 前端运行 demo,你可以利用他轻松生成你想要生成的图像,并尝试不同组合。
import gradio as gr
from pathlib import Path
import openvino as ov
import numpy as np
core = ov.Core()
model_dir = Path("./sdxl_vino_model")
# 如果你只有量化前模型,请使用这个地址并注释 optimized_unet 地址:
# UNET_PATH = model_dir / "unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
UNET_PATH = model_dir / "optimized_unet" / "openvino_model.xml"
from optimum.intel.openvino import OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline
text2image_pipe = OVStableDiffusionXLPipeline.from_pretrained(model_dir)
text2image_pipe.unet.model = core.read_model(UNET_PATH)
text2image_pipe.unet.request = core.compile_model(text2image_pipe.unet.model)
def generate_from_text(text, seed, num_steps, height, width):
result = text2image_pipe(text, num_inference_steps=num_steps, guidance_scale=0.0, generator=np.random.RandomState(seed), height=height, width=width).images[0]
return result
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
with gr.Column():
positive_input = gr.Textbox(label="Text prompt")
with gr.Row():
seed_input = gr.Number(precision=0, label="Seed", value=42, minimum=0)
steps_input = gr.Slider(label="Steps", value=1, minimum=1, maximum=4, step=1)
height_input = gr.Slider(label="Height", value=512, minimum=256, maximum=1024, step=32)
width_input = gr.Slider(label="Width", value=512, minimum=256, maximum=1024, step=32)
btn = gr.Button()
out = gr.Image(label="Result (Quantized)" , type="pil", width=512)
btn.click(generate_from_text, [positive_input, seed_input, steps_input, height_input, width_input], out)
gr.Examples([
["cute cat", 999],
["underwater world coral reef, colorful jellyfish, 35mm, cinematic lighting, shallow depth of field, ultra quality, masterpiece, realistic", 89],
["a photo realistic happy white poodle dog playing in the grass, extremely detailed, high res, 8k, masterpiece, dynamic angle", 1569],
["Astronaut on Mars watching sunset, best quality, cinematic effects,", 65245],
["Black and white street photography of a rainy night in New York, reflections on wet pavement", 48199]
], [positive_input, seed_input])
try:
demo.launch(debug=True)
except Exception:
demo.launch(share=True, debug=True) 总结
利用最新版本的 OpenVINO™ 优化,我们可以很容易实现在家用设备上高效推理图像生成 AI 的能力,加速生成式 AI 在世纪场景下的落地应用;欢迎您与我们一同体验 OpenVINO™ 与 NNCF 在生成式 AI 场景上的强大威力。



