使用AsyncInferQueue进一步提升AI推理程序的吞吐量
 openlab_4276841a
更新于 2年前
openlab_4276841a
更新于 2年前
作者: 战鹏州 英特尔物联网行业创新大使
本文将介绍基于OpenVINO的异步推理队列类AyncInferQueue,启动多个(>2)推理请求(infer request),帮助读者在硬件投入不变的情况下,进一步提升AI推理程序的吞吐量(Throughput)。
在阅读本文前,请读者先了解使用start_async()和wait()方法实现基于2个推理请求的异步推理实现方式。该异步推理实现方式相对于同步推理方式,极大提升了AI推理程序的吞吐量,但从任务管理器中可以看到,AI推理硬件的利用率还有很大的提升空间。
这意味着,AI推理硬件还有潜力可挖,可以通过进一步提高推理请求个数来提升AI推理硬件的利用率,从而提高AI推理程序的吞吐量。
1.1推理请求(InferRequest)和流(stream)
OpenVINO运行时(Runtime)用推理请求(infer request)来抽象在指定计算设备上运行已编译模型(Compiled_Model)。从编写程序的角度看,推理请求是一个类,封装了支持推理请求以同步或异步方式运行的属性和方法。推理请求(InferRequest)类的详细定义参考:https://github.com/openvinotoolkit/openvino/blob/master/src/inference/include/openvino/runtime/infer_request.hpp#L34
推理请求的个数,由开发者定义;但计算设备能并行处理的推理请求个数,由硬件本身的处理单元(Processing Unit)决定。超过计算硬件并行处理数量的推理请求,会被计算硬件用队列储存起来,当计算硬件空闲后,队列中的推理请求将被依次取出并执行。
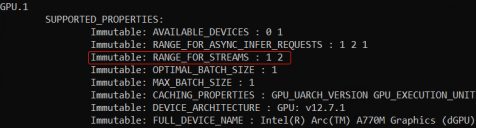
OpenVINO用流(stream)来抽象计算设备能并行处理推理请求的能力,通过属性:“NUM_STREAMS”,可以获取延迟优先或吞吐量优先模式下的计算硬件支持的最优streams数量,如下表所示。
[1]:上述数据在蝰蛇峡谷上测得,CPU=i7-12700H, 集成显卡=Iris Xe, 独立显卡=A770m
[2]: GPU设备没有INFERENCE_NUM_THREADS属性
上述数据测试的源代码如下,欢迎各位读者在自己的硬件平台上测试:
from openvino.runtime import Core, get_version
core = Core()
print(get_version())
print(core.available_devices)
device = device = ['GPU.0', 'GPU.1', 'CPU', 'AUTO', 'AUTO:GPU,-CPU'][0]
cfgs = {}
cfgs['PERFORMANCE_HINT'] = ['THROUGHPUT', 'LATENCY', 'CUMULATIVE_THROUGHPUT'][0]
net = core.compile_model("model.onnx",device,cfgs)
# Get Supported properties
supported_properties = net.get_property('SUPPORTED_PROPERTIES')
print(f'Support properties for {device}:', supported_properties)
opt_nireq = net.get_property('OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS')
print(f'OPTIMAL_NUMBER_OF_INFER_REQUESTS for {device}:', opt_nireq)
nstreams = net.get_property('NUM_STREAMS')
print(f'nstreams for {device}:', nstreams)
performance_hint_num_requests = net.get_property('PERFORMANCE_HINT_NUM_REQUESTS')
print(f'performance_hint_num_requests for {device}:', performance_hint_num_requests)
if device == "CPU":
# INFERENCE_NUM_THREADS
inference_num_threads = net.get_property('INFERENCE_NUM_THREADS')
print(f'inference_num_threads for {device}:', inference_num_threads)
else:
gpu_queue_priority = net.get_property('GPU_QUEUE_PRIORITY')
print(f'GPU queue priority for {device}:', gpu_queue_priority) 1.1.1CPU的流与推理请求
对于CPU来说,一个流(stream)只能服务一个推理请求。通过属性ov::range_for_streams,可以查到CPU支持的流数量的范围;流的数量无需开发者使用代码显示设置,OpenVINO运行时会根据延迟优先或吞吐量优先来自动设置。 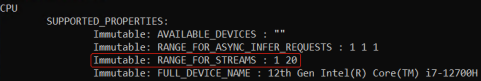
1.1.2GPU的流与推理请求
对于GPU来说,一个流(stream)可以同时服务两个推理请求。通过属性ov::range_for_streams,可以查到GPU支持的流数量的范围:[1, 2];流的数量无需开发者使用代码显示设置,OpenVINO运行时会根据延迟优先或吞吐量优先来自动设置。
参考代码: https://www.jianshu.com/p/1748444e6a50
1.2AsyncInferQueue类
OpenVINO运行时(Runtime)提供AsyncInferQueue类来抽象并管理异步推理请求池,其常用方法和属性有:__init__(self, compiled_model, jobs = 0):创建AsyncInferQueue对象
set_callback(func_name):为推理请求池中所有的推理请求设置统一的回调函数
start_async(inputs, userdata = None):异步启动推理请求
wait_all():等待所有的推理请求执行完毕
1.2.1基于AsyncInferQueue类的异步推理范例程序
基于AsyncInferQueue类YOLOv5模型的异步推理范例程序的核心代码部分如下所示:完整范例代码请下载:yolov5_async_infer_queue.py
运行代码前,请参考运行环境搭建流程。
...
def preprocess(frame):
# Preprocess the frame
letterbox_im, _, _= letterbox(frame, auto=False) # preprocess frame by letterbox
im = letterbox_im.transpose((2, 0, 1))[::-1] # HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB
im = np.float32(im) / 255.0 # 0 - 255 to 0.0 - 1.0
blob = im[None] # expand for batch dim
return blob, letterbox_im.shape[:-1], frame.shape[:-1]
def postprocess(ireq: InferRequest, user_data: tuple):
result = ireq.results[ireq.model_outputs[0]]
dets = non_max_suppression(torch.tensor(result))[0].numpy()
bboxes, scores, class_ids= dets[:,:4], dets[:,4], dets[:,5]
# rescale the coordinates
bboxes = scale_coords(user_data[1], bboxes, user_data[2]).astype(int)
print(user_data[0],"\t"+f"{ireq.latency:.3f}"+"\t", class_ids)
return
# Step1: Initialize OpenVINO Runtime Core
core = Core()
# Step2: Build compiled model
device = device = ['GPU.0', 'GPU.1', 'CPU', 'AUTO', 'AUTO:GPU,-CPU'][0]
cfgs = {}
cfgs['PERFORMANCE_HINT'] = ['THROUGHPUT', 'LATENCY', 'CUMULATIVE_THROUGHPUT'][0]
net = core.compile_model("yolov5s.xml",device,cfgs)
output_node = net.outputs[0]
b,n,input_h,input_w = net.inputs[0].shape
# Step3: Initialize InferQueue
ireqs = AsyncInferQueue(net)
print('Number of infer requests in InferQueue:', len(ireqs))
# Step3.1: Set unified callback on all InferRequests from queue's pool
ireqs.set_callback(postprocess)
# Step4: Read the images
image_folder = "./data/images/"
image_files= os.listdir(image_folder)
print(image_files)
frames = []
for image_file in image_files:
frame = cv2.imread(os.path.join(image_folder, image_file))
frames.append(frame)
# 4.1 Warm up
for id, _ in enumerate(ireqs):
# Preprocess the frame
start = perf_counter()
blob, letterbox_shape, frame_shape = preprocess(frames[id % 4])
end = perf_counter()
print(f"Preprocess {id}: {(end-start):.4f}.")
# Run asynchronous inference using the next available InferRequest from the pool
ireqs.start_async({0:blob},(id, letterbox_shape, frame_shape))
ireqs.wait_all()
# Step5: Benchmark the Async Infer
start = perf_counter()
in_fly = set()
latencies = []
niter = 16
for i in range(niter):
# Preprocess the frame
blob, letterbox_shape, frame_shape = preprocess(frames[i % 4])
idle_id = ireqs.get_idle_request_id()
if idle_id in in_fly:
latencies.append(ireqs[idle_id].latency)
else:
in_fly.add(idle_id)
# Run asynchronous inference using the next available InferRequest from the pool
ireqs.start_async({0:blob},(i, letterbox_shape, frame_shape) )
ireqs.wait_all()
运行结果如下所示,与基于单个推理请求的start_async()+wait()实现方式相比,基于AsyncInferQueue类的YOLOv5模型的异步推理程序的吞吐量明显得到提升。